Did you know your smartphone probably knows you better than your best friend? It goes everywhere with you, hears your conversations (sometimes even joins in!), and tracks everything you do online.
Kinda makes you think, doesn’t it?
We rely on these pocket-sized computers for everything these days, but have you ever stopped to consider the cost of convenience? All those apps we love? They’re often collecting a ton of data about us.
This blog is your guide to navigating the complex world of smartphone privacy. We’ll be exploring questions like:
- What information are your apps really collecting?
- How is your location data being used?
- Are your private conversations truly private?
We’ll also share practical tips and tricks to help you take control of your data and protect your privacy. Because in the age of smartphones, knowledge is power.

Let’s dive in!
The Evolution of Smartphone Privacy Concerns
When smartphones first gained popularity, privacy concerns were minimal. Early phones had limited functionality and users typically relied on them for calls, texts, and a few basic apps. However, as smartphones became more advanced, so did the privacy risks associated with them. Today, smartphones are packed with sensors, GPS tracking, and microphones that can collect vast amounts of data.
The rise of smartphones also coincided with the growth of data-driven business models, where companies like Google, Facebook, and others began to monetize user data. This shift transformed smartphones from communication devices into powerful data-gathering tools. The more advanced they became, the more data they could collect.
With this, privacy concerns began to grow. Governments introduced surveillance measures, corporations collected personal information for targeted advertising, and cybercriminals developed sophisticated methods to exploit vulnerabilities. The evolution of smartphone technology has thus been accompanied by a corresponding evolution in privacy concerns.
Types of Data Collected by Smartphones
Smartphones collect a wide range of personal data, often without users even realizing it. Understanding what type of data your device is gathering can help you take steps to protect it.
1. Location Data
Your smartphone continuously tracks your location through GPS, Wi-Fi, and cell towers. Apps that provide services like navigation, weather, and location-based recommendations rely on this data. However, this data is also highly sensitive and can be used to build a detailed profile of your movements and habits.
2. Personal Communication
Messages, emails, and phone calls are some of the most personal data stored on your phone. Messaging apps, even encrypted ones, may store metadata about your conversations, such as who you’re talking to, when, and how frequently.
3. Browser History
Just like computers, smartphones store browsing history, search queries, and cookies. This data can be used by advertisers to target you with relevant ads or by malicious actors to track your online behavior.
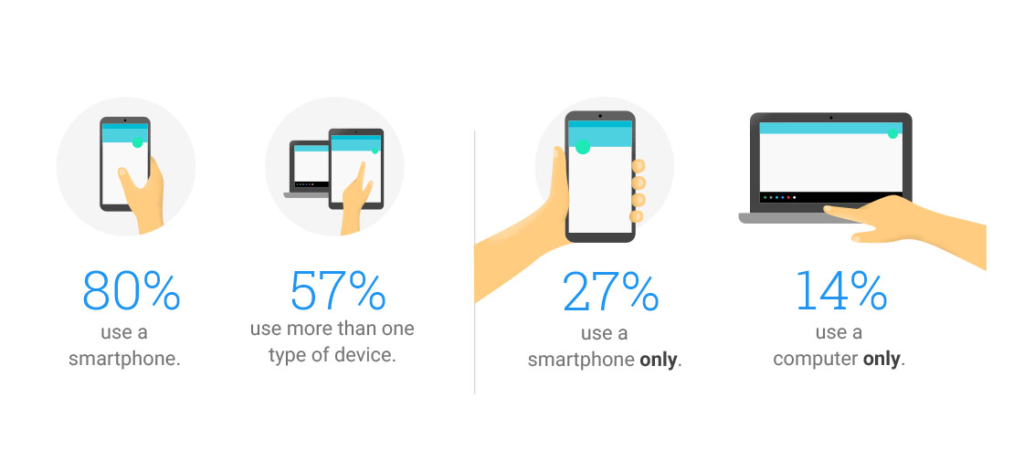
4. App Usage Data
Apps on your phone can gather information about how and when you use them. This can include which apps you use most frequently, how much time you spend on them, and even your interactions within the app.
5. Biometric Data
Many modern smartphones now come equipped with biometric sensors, such as fingerprint scanners and facial recognition technology. While these features add a layer of security, they also introduce new privacy concerns regarding how this sensitive data is stored and used.
6. Financial Data
With the growth of mobile banking and payment services, smartphones now hold vast amounts of financial data. From credit card information to transaction histories, your phone is a treasure trove of sensitive financial information that needs to be protected.
Major Privacy Threats With Smartphones
Smartphones are vulnerable to a variety of privacy threats, many of which are sophisticated and difficult to detect. Here are some of the most common threats that smartphone users face:
1. Malware and Spyware
Malicious software can be installed on your phone to steal your data, track your location, or even eavesdrop on your conversations. Malware can come from malicious apps, phishing attacks, or even compromised websites.
2. App Permissions Abuse
Many apps request access to data that they don’t necessarily need. For example, a flashlight app might ask for access to your location, contacts, and camera. This data can then be sold to third parties, used for targeted advertising, or worse, stolen by hackers.
3. Wi-Fi Snooping
When you connect to public Wi-Fi networks, your data is at risk of being intercepted by cybercriminals. These attackers can use “man-in-the-middle” attacks to spy on your internet traffic, steal login credentials, and monitor your online activities.

4. SIM Card Swapping
SIM card swapping is a growing threat where hackers trick mobile carriers into transferring your phone number to a different SIM card. Once they have control of your number, they can intercept two-factor authentication codes and access your online accounts.
5. Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are one of the most common ways hackers steal personal information. These attacks can come in the form of text messages, emails, or fake websites that trick users into giving away their passwords, credit card details, or other sensitive information.
6. Government Surveillance
Governments around the world have implemented various forms of digital surveillance, often using smartphones as a primary source of data. While some of these measures are designed to protect national security, they can also lead to an invasion of privacy if not properly regulated.
How to Protect Your Smartphone Privacy
While smartphone privacy threats are real, there are many steps you can take to protect your personal data. Below are some best practices to help safeguard your privacy.
1. Use Strong Passwords and Biometric Authentication
One of the easiest ways to protect your phone is by using a strong password or PIN. Avoid using common passwords like “1234” or “password” and enable biometric authentication like fingerprints or facial recognition for added security.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication provides an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification in addition to your password. Many services now offer 2FA, and it’s highly recommended to enable it wherever possible.
3. Manage App Permissions
Review the permissions that apps request and only grant access to data that is essential for the app to function. If an app asks for permissions that seem unnecessary, such as a game requesting access to your contacts, consider uninstalling it.
READ MORE – How to Make the Best Use of Your Smartphones: 40 Expert Tips & Tricks
4. Use a VPN on Public Wi-Fi
Whenever you connect to a public Wi-Fi network, make sure to use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to encrypt your internet traffic. A VPN can help protect your data from being intercepted by cybercriminals on unsecure networks.
5. Encrypt Your Data
Most modern smartphones offer the option to encrypt your data, which ensures that your personal information remains secure even if your phone is lost or stolen. Encryption scrambles your data so that only authorized parties can access it.
6. Keep Your Software Updated
Regularly updating your phone’s operating system and apps is crucial for maintaining security. Updates often include patches for vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers, so it’s important to stay up to date.
7. Use Secure Messaging Apps
If you want to protect your private conversations, use secure messaging apps that offer end-to-end encryption. This ensures that only you and the recipient can read the messages, and not even the app provider can access them.
8. Avoid Clicking on Suspicious Links
Be cautious of any unsolicited messages or emails that ask you to click on a link or download an attachment. These could be phishing attempts designed to steal your personal information.
9. Turn Off Unnecessary Features
Features like GPS, Bluetooth, and NFC can make your phone more vulnerable to attacks. When you’re not using these features, it’s a good idea to turn them off to reduce the risk of unauthorized access to your device.

What’s the Role of Smartphone Manufacturers in Privacy Protection?
Smartphone manufacturers play a critical role in protecting user privacy. From the way phones are designed to how they handle software updates, manufacturers can significantly influence the level of privacy users experience.
1. Privacy-Focused Operating Systems
Some smartphone manufacturers, like Apple, place a strong emphasis on privacy and offer operating systems that are designed with user privacy in mind. Apple, for example, has implemented features like app transparency that requires apps to get explicit permission from users before tracking their activity across different apps and websites.
2. Regular Security Updates
Manufacturers are responsible for releasing security patches and updates to protect users from newly discovered vulnerabilities. Regular updates ensure that smartphones are equipped with the latest protections, reducing the risk of cyberattacks.
3. Data Minimization
Some manufacturers have adopted data minimization practices, which involve collecting only the data that is necessary for the functioning of the phone or specific features. This reduces the amount of personal information stored on devices, minimizing the potential impact of data breaches.
4. Transparency and User Control
Manufacturers can enhance privacy by giving users more control over their data. For example, Apple’s iOS allows users to review app permissions and easily toggle off access to sensitive information like location and contacts. By providing transparency and user-friendly privacy controls, manufacturers can help users protect their personal information.
5. Security Hardware
Some manufacturers are now incorporating hardware-based security features, such as secure enclaves or dedicated security chips, that store sensitive data like biometric information separately from the rest of the phone’s memory. This adds an extra layer of protection in case of malware attacks or physical theft.
App Developers and Privacy
App developers also play a significant role in ensuring smartphone privacy. While many apps require access to certain data to function properly, developers must balance functionality with user privacy.
1. Data Collection Practices
App developers need to follow ethical data collection practices, collecting only the data that is necessary for the app’s operation. For example, a weather app may need access to your location, but it shouldn’t require access to your photos or contacts.
2. Encryption and Security Protocols
Developers should implement strong encryption protocols to protect the data that their apps handle. This includes encrypting data in transit (when it’s being sent between the phone and the app’s servers) and at rest (when it’s stored on the phone).

3. Compliance with Privacy Laws
With regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), developers must ensure that their apps comply with privacy laws. This includes giving users the ability to delete their data, opt out of tracking, and providing clear privacy policies.
4. User Education
Developers should make an effort to educate users about the data their apps collect and how it’s used. This can be done through clear, easy-to-understand privacy policies and in-app notifications that explain the permissions being requested.
Privacy Policies and Terms of Service
Most users don’t bother to read privacy policies and terms of service agreements when installing apps or using new services. However, these documents often contain important information about how your data will be used, shared, and stored.
1. What to Look for in Privacy Policies
When reviewing privacy policies, look for sections that explain what data the app collects, how it’s used, and whether it’s shared with third parties. Be particularly cautious of apps that sell your data to advertisers or other third parties.
2. Terms of Service Agreements
Terms of service agreements often contain information about your rights as a user and the legal obligations of the company providing the service. Pay attention to sections that address dispute resolution, liability, and the company’s ability to change the terms without notice.
3. Common Loopholes
Some companies include loopholes in their privacy policies that allow them to collect and share data in ways that users might not expect. For example, a company might claim that it only collects anonymous data, but in reality, the data can be re-identified with minimal effort.
Government Surveillance and Smartphone Privacy
Smartphone privacy is not just about protecting your data from hackers and app developers; it’s also about safeguarding your information from government surveillance. Governments around the world have implemented various forms of digital surveillance, often using smartphones as a primary source of data.
1. The Role of National Security Agencies
Agencies like the NSA in the United States and GCHQ in the UK have been known to conduct mass surveillance programs that collect data from smartphones. While these programs are often justified as necessary for national security, they raise significant privacy concerns.

2. Metadata Collection
One of the most common forms of government surveillance is the collection of metadata, which includes information about who you’re communicating with, when, and where, but not the content of the communications themselves. Metadata can be used to build detailed profiles of individuals, even without accessing the actual content of their messages.
3. The Role of Encryption in Protecting Privacy
Encryption is one of the most effective tools for protecting smartphone privacy from government surveillance. By encrypting data, users can prevent unauthorized parties, including government agencies, from accessing their personal information.
4. Balancing Privacy and National Security
Governments often argue that mass surveillance is necessary to protect national security, but privacy advocates argue that these programs are invasive and undermine fundamental rights. The challenge is finding a balance between protecting individual privacy and ensuring national security.
Emerging Privacy Technologies
As smartphone privacy concerns grow, new technologies are emerging to help users protect their data. Below are some of the most promising developments in this field.
1. Decentralized Identity Systems
Decentralized identity systems use blockchain technology to give users control over their personal data. Instead of relying on centralized companies to store your information, these systems allow you to store your data on a decentralized network and only share it with trusted parties.
2. AI-Powered Privacy Tools
Artificial intelligence is being used to develop tools that can automatically detect and block privacy threats. For example, AI can be used to identify malicious apps, block phishing attacks, and detect suspicious activity on your phone.
3. Zero-Knowledge Encryption
Zero-knowledge encryption is a type of encryption where the service provider doesn’t have access to the encryption keys, meaning that they can’t read your data even if they wanted to. This ensures that only you have access to your personal information.
4. Privacy-Focused Browsers
Several browsers, such as DuckDuckGo and Brave, are designed with privacy in mind. These browsers block trackers, prevent fingerprinting, and offer built-in VPN services to protect your privacy while browsing the web.
The Future of Smartphone Privacy
Smartphone privacy will continue to evolve as technology advances. Here are some trends to watch for in the coming years:
1. Increased Regulation
As public awareness of smartphone privacy issues grows, governments are likely to introduce more stringent regulations to protect user data. Laws like GDPR and CCPA are just the beginning, and more countries are expected to follow suit.
2. Smarter Privacy Controls
Smartphone manufacturers and app developers will likely introduce more advanced privacy controls that give users greater control over their data. This could include features like real-time privacy audits and more granular control over app permissions.

3. The Rise of Privacy-First Devices
As privacy becomes a more significant concern, we can expect to see more devices designed with privacy in mind. These devices will likely come with enhanced security features, better encryption, and minimal data collection by default.
4. User-Driven Data Ownership
The future of smartphone privacy may involve users having full ownership of their data. Instead of companies controlling and profiting from user data, individuals could have the power to decide who gets access to their information and how it’s used.
Do You Believe in Smartphone Privacy?
Smartphone privacy is a complex and multifaceted issue that touches on everything from app permissions to government surveillance. As our devices become more integrated into our daily lives, the need to protect our personal information grows increasingly urgent.
By understanding the types of data collected by smartphones, recognizing the major privacy threats, and taking proactive steps to safeguard your information, you can better protect your privacy in an increasingly connected world.
The future of smartphone privacy will be shaped by new technologies, evolving regulations, and growing public awareness. While the challenges are significant, the tools and strategies for protecting your data are also becoming more sophisticated. By staying informed and taking control of your digital footprint, you can enjoy the benefits of smartphone technology without sacrificing your privacy.
You might also be interested in – What Are the Top 10 Android Smartphones in 2024?


