You’ve seen the ads, the promises, the glowing testimonials. Magnesium glycinate is the new it-supplement, a magical potion that’s supposed to cure everything from insomnia to anxiety.
But is it really all it’s cracked up to be?
Let’s face it, the supplement world is a jungle. With countless products claiming to be the next big thing, it’s hard to know what’s worth your money and what’s just empty promises. So, we’re on a mission to cut through the noise and give you the straight talk about magnesium glycinate.
We’re going to dig deep into the science, separate the facts from the fiction, and uncover the truth about this popular supplement. Is it a miracle worker or just another hyped-up product? Get ready to unlock the secrets of glycinate.

Understanding Magnesium and Its Importance
The Role of Magnesium in the Body
Common Dietary Sources of Magnesium
Chemical Composition and Bioavailability
Comparison with Other Forms of Magnesium
What Are the Benefits of Magnesium Glycinate?
Myth 1: All Magnesium Supplements are the Same
Myth 2: Magnesium Glycinate Causes Digestive Issues
Myth 3: Magnesium Glycinate is Only for Sleep and Anxiety
Myth 4: You Can Get Enough Magnesium from Diet Alone
Myth 5: Magnesium Glycinate is Only for Those with a Deficiency
Scientific Evidence and Studies
Clinical Trials on Magnesium Glycinate
Meta-Analyses and Systematic Reviews
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Integrating Magnesium Glycinate into Your Routine
Tips for Effective Supplementation
Should You Go for Magnesium Glycinate?
Understanding Magnesium and Its Importance
The Role of Magnesium in the Body
Magnesium is the fourth most abundant mineral in the human body and is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions. It is vital for:
- Energy Production: Magnesium is a cofactor in ATP (adenosine triphosphate) production, which is the primary energy currency of cells.
- Protein Synthesis: It helps in the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and proteins.
- Muscle and Nerve Function: Magnesium is essential for the regulation of muscle contractions and nerve transmission.
- Bone Health: About 60% of the body’s magnesium is stored in the bones, where it plays a role in bone structure and calcium metabolism.
- Blood Glucose Control: Magnesium helps regulate blood sugar levels and is crucial for insulin function.
- Cardiovascular Health: It maintains a regular heartbeat and prevents the formation of blood clots.

Common Dietary Sources of Magnesium
While magnesium is found in various foods, modern diets often fall short of providing adequate amounts. Common sources include:
- Leafy green vegetables (e.g., spinach, kale)
- Nuts and seeds (e.g., almonds, pumpkin seeds)
- Whole grains (e.g., brown rice, quinoa)
- Legumes (e.g., black beans, lentils)
- Fish (e.g., mackerel, salmon)
Despite these sources, studies suggest that a significant portion of the population may not meet their daily magnesium requirements, leading to a need for supplementation.
Read More: How to Use AI Logo Generators to Enhance Your Brand Identity
What is Magnesium Glycinate?
Chemical Composition and Bioavailability
Magnesium , also known as magnesium bisglycinate, is a compound consisting of magnesium bound to glycine, an amino acid. This chelated form is known for its high bioavailability, meaning it is well-absorbed and utilized by the body. The glycine component not only enhances absorption but also has calming properties, making magnesium a popular choice for those with anxiety or sleep disorders.

Comparison with Other Forms of Magnesium
There are several forms of magnesium supplements available, each with varying degrees of absorption and specific uses:
- Magnesium Oxide: Common but has low bioavailability; often used for its laxative effect.
- Magnesium Citrate: Better absorbed than oxide; used for muscle relaxation and constipation relief.
- Magnesium Chloride: High absorption rate; used for detoxification and improving digestion.
- Magnesium Sulfate: Known as Epsom salt; used topically for muscle soreness.
- Magnesium L-Threonate: Specifically noted for its ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier and improve cognitive function.
Magnesium glycinate is often preferred for its gentle effect on the stomach and its ability to address both magnesium deficiency and related health issues without causing digestive distress.
What Are the Benefits of Magnesium Glycinate?
Improved Sleep Quality
Magnesium plays a pivotal role in regulating neurotransmitters that are involved in sleep, such as GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). Magnesium glycinate, with its added glycine component, can further enhance sleep quality by promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety. Studies have shown that magnesium supplementation can improve sleep onset, duration, and quality, particularly in older adults and those with insomnia.
Anxiety and Stress Reduction
Magnesium is essential for the function of the HPA (hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal) axis, which controls the body’s response to stress. A deficiency in magnesium can exacerbate stress and anxiety. Magnesium glycinate’s high bioavailability ensures effective replenishment of magnesium levels, which can help mitigate symptoms of anxiety and promote a sense of calm.

Muscle and Joint Health
Athletes and individuals with muscle cramps or spasms can benefit from magnesium glycinate due to its role in muscle function and relaxation. Magnesium helps regulate muscle contractions and prevents excessive calcium buildup in muscles, which can cause cramps. Furthermore, glycine is known to support joint and connective tissue health, making magnesium glycinate beneficial for overall musculoskeletal well-being.
Cardiovascular Health
Magnesium is critical for maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system. It helps regulate heart rhythm, supports healthy blood pressure levels, and prevents the formation of blood clots. Studies have shown that magnesium supplementation can reduce the risk of hypertension and support overall heart health. Magnesium glycinate, with its superior absorption, is particularly effective in addressing cardiovascular concerns.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Magnesium plays a role in insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Low magnesium levels are associated with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Supplementing with magnesium glycinate can improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar levels, making it a valuable tool for managing diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
Bone Health
Magnesium is a key component of bone mineralization and influences the activities of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone formation and resorption. Adequate magnesium intake is crucial for maintaining bone density and preventing osteoporosis. Magnesium glycinate, with its high bioavailability, ensures efficient delivery of magnesium to the bones.
Debunking Common Myths
Myth 1: All Magnesium Supplements are the Same
One of the most prevalent myths is that all magnesium supplements are created equal. In reality, different forms of magnesium vary significantly in their absorption rates, bioavailability, and specific health benefits. Magnesium glycinate stands out due to its high absorption rate and gentle effect on the digestive system, making it a superior choice for addressing magnesium deficiency and related health issues.
Myth 2: Magnesium Glycinate Causes Digestive Issues
Some people worry that magnesium supplements can cause digestive problems such as diarrhea or stomach cramps. While this can be true for certain forms like magnesium oxide or citrate, magnesium glycinate is known for its gentle effect on the stomach. Its chelated form minimizes the risk of digestive distress, making it suitable for individuals with sensitive stomachs.
Myth 3: Magnesium Glycinate is Only for Sleep and Anxiety
While magnesium glycinate is indeed effective for improving sleep and reducing anxiety, its benefits extend far beyond these areas. From muscle health and cardiovascular support to blood sugar regulation and bone health, magnesium glycinate plays a multifaceted role in promoting overall well-being.
Myth 4: You Can Get Enough Magnesium from Diet Alone
Although it is possible to obtain magnesium from dietary sources, many people do not consume sufficient amounts due to modern agricultural practices, soil depletion, and dietary habits. As a result, magnesium deficiency is relatively common. Supplementation with magnesium glycinate can help bridge this gap and ensure adequate magnesium levels for optimal health.
Myth 5: Magnesium Glycinate is Only for Those with a Deficiency
Even individuals without a diagnosed magnesium deficiency can benefit from magnesium glycinate supplementation. Given its wide range of health benefits, including improved sleep, stress reduction, and cardiovascular support, magnesium glycinate can be a valuable addition to a wellness regimen for overall health maintenance and disease prevention.
READ MORE : What is Buzzcast: Everything You Need to Know
Scientific Evidence and Studies
Clinical Trials on Magnesium Glycinate
Numerous clinical trials have explored the efficacy of magnesium glycinate in various health conditions. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine found that magnesium supplementation improved sleep quality in older adults with insomnia. Another study in the Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine reported that magnesium supplementation reduced symptoms of anxiety and depression in adults.

Meta-Analyses and Systematic Reviews
Meta-analyses and systematic reviews have also highlighted the benefits of magnesium supplementation. A meta-analysis published in the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition concluded that magnesium supplementation has a beneficial effect on blood pressure. Another review in Diabetes Care found that higher magnesium intake is associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes.
Expert Opinions
Health experts and nutritionists often recommend magnesium glycinate for its superior absorption and effectiveness. Dr. Carolyn Dean, a well-known authority on magnesium, emphasizes the importance of magnesium glycinate for addressing magnesium deficiency and supporting overall health. Similarly, Dr. Mark Hyman, a functional medicine practitioner, advocates for the use of magnesium glycinate to manage stress and improve sleep.
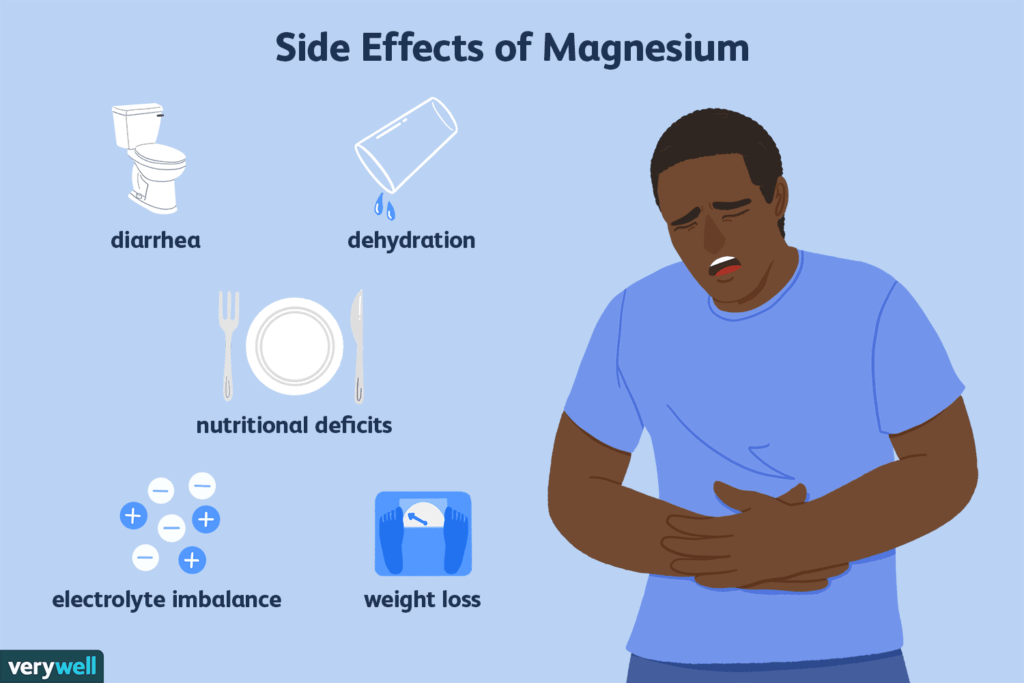
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Common Side Effects
While magnesium glycinate is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as:
- Drowsiness or lethargy (beneficial for those seeking improved sleep)
- Mild gastrointestinal discomfort (rare with glycinate form)
READ MORE- 20 Famous Bollywood Love Stories That Met A Tragic End
Precautions and Interactions
Individuals with kidney disease should consult their healthcare provider before taking magnesium supplements, as impaired kidney function can affect magnesium excretion. Additionally, magnesium supplements may interact with certain medications, such as antibiotics and diuretics. It’s essential to discuss supplementation with a healthcare provider, especially if taking prescription medications.
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of magnesium glycinate varies depending on individual needs and health conditions. Generally, a dosage of 200-400 mg of elemental magnesium per day is considered safe and effective for most adults. It’s best to start with a lower dose and gradually increase as needed, monitoring for any adverse effects.
Integrating Magnesium Glycinate into Your Routine
Choosing the Right Supplement
When selecting a magnesium glycinate supplement, look for products that provide clear information on the amount of elemental magnesium per serving. Opt for reputable brands that adhere to good manufacturing practices and have third-party testing for quality and purity.
Tips for Effective Supplementation
- Timing: Take magnesium glycinate in the evening to support relaxation and improve sleep quality.
- Consistency: Consistent supplementation is key to reaping the benefits of magnesium glycinate.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to support magnesium absorption and overall health.
- Balanced Diet: Complement supplementation with a balanced diet rich in magnesium-containing foods.

Lifestyle Considerations
Incorporate other lifestyle practices to enhance the benefits of magnesium glycinate, such as:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity supports overall health and enhances the effectiveness of supplementation.
- Stress Management: Practices like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can amplify the calming effects of magnesium.
- Sleep Hygiene: Maintain a regular sleep schedule and create a restful sleep environment to maximize the sleep-promoting benefits of magnesium glycinate.
Should You Go for Magnesium Glycinate?
Magnesium glycinate is a highly effective form of magnesium supplementation, offering a range of health benefits from improved sleep and reduced anxiety to enhanced muscle, cardiovascular, and bone health. By understanding the myths and facts surrounding magnesium glycinate, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and wellness. With its superior bioavailability and gentle effect on the stomach, magnesium glycinate is a valuable tool for addressing magnesium deficiency and promoting overall well-being.
Incorporating magnesium glycinate into your daily routine, along with a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle practices, can help you achieve optimal health and prevent a range of chronic conditions. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure it is appropriate for your individual health needs.
You might also be interested in – What is Digital Detox & Why Do You Need It?


