Ever dreamt of turning those market charts into a steady stream of profits and turning a trading pro? Or maybe you’re just curious about how the whole trading game works. Well, you’ve landed in the right spot.
This blog is your all-access pass to the exciting world of trading. We’ll break down complex strategies, share insider tips, and guide you every step of the way as you transform from a trading newbie to a seasoned pro.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or have dipped your toes in the market before, get ready for an adventure. We’ll cover everything from the basics of stocks and options to advanced technical analysis and risk management.
Let’s dive in and discover the secrets of successful trading!
1. Understand the Fundamentals of Trading
Before even thinking about being a trading pro, it’s essential to master the basics of how financial markets function. Understanding these foundational elements will help you recognize opportunities and avoid common pitfalls.
Key Market Concepts to Master
- Market Structure: Financial markets are decentralized arenas where buyers and sellers exchange assets. Understanding the nuances of different markets (such as stock markets, forex, commodities) is vital because each behaves differently. For example, the stock market is influenced heavily by company earnings and economic data, while the forex market is more reactive to macroeconomic factors like interest rates and geopolitical events.
- Order Types: There are various order types in trading, and knowing how to use them efficiently is critical:
- Market Orders: Execute immediately at the current market price.
- Limit Orders: Execute only when the price reaches a specific level.
- Stop Orders: Trigger an order only after a specified price is reached, typically used for stop-loss or entry orders.
- Stop-Limit Orders: A combination of stop and limit orders, where the order becomes a limit order when the stop price is reached.
- Leverage and Margin: Leverage allows trading pros to control large positions with a small amount of capital, magnifying both gains and losses. For example, in forex, brokers often offer 50:1 leverage, meaning you can control $50,000 with just $1,000. Margin is the money you borrow to increase your position size, but with great power comes great risk. Understanding the margin requirements of your broker and how to manage leverage is crucial for capital preservation.

Grasp the Different Market Environments
Markets can broadly be classified into two types:
- Bull Markets: Where prices rise and investor confidence is high.
- Bear Markets: Where prices fall and pessimism dominates.
A trading pro can profit in both environments by using different strategies, such as short-selling during bear markets or buying the dip during bull markets. Learning to recognize these cycles and adjusting your strategies accordingly is a hallmark of professional trading.
READ MORE: How to Resolve Clogged Radiators in Cars: Symptoms, Causes, and Solutions
2. Choose Your Trading Style
Your trading style should align with your financial goals, available time, and personality. Choosing the right trading style from the outset is critical because it dictates your approach to analysis, risk management, and daily activities.
Exploring Popular Trading Styles in Detail
Day Trading: Fast-Paced and Intense
- Time Commitment: Full-time trading pros who can monitor charts throughout the day.
- Holding Period: Seconds to hours, closing positions by the end of the trading day.
- Key Requirements: Day trading requires discipline, quick decision-making, and access to real-time data and advanced charting tools.
- Strategy Example: Momentum trading, where trading pros buy stocks showing strong upward momentum and sell as soon as the momentum fades. It relies heavily on technical analysis and real-time data.

Swing Trading: Capturing Medium-Term Trends
- Time Commitment: Part-time or full-time traders with the ability to monitor markets at least once per day.
- Holding Period: Days to weeks.
- Key Requirements: Patience and the ability to wait for trades to mature. Swing traders often rely on both technical and fundamental analysis to identify medium-term trends.
- Strategy Example: Trend following, where trading pros identify trends (e.g., uptrend or downtrend) and buy in the direction of the trend. Confirmation from indicators like the moving average can help reduce false signals.
Position Trading: Long-Term Strategic Thinking
- Time Commitment: Minimal daily commitment; regular updates every few days or weeks.
- Holding Period: Weeks to months or even years.
- Key Requirements: A deep understanding of macroeconomic trends and fundamental analysis. Position traders typically ride out market volatility and rely on broader economic or company-based developments.
- Strategy Example: Holding growth stocks with strong fundamentals over a long period, profiting from both capital gains and dividends.
Scalping: Quick, Small Wins
- Time Commitment: Full-time trading pros who can execute dozens to hundreds of trades in a day.
- Holding Period: Seconds to minutes.
- Key Requirements: Fast execution, minimal slippage, and a low commission broker. Scalpers capitalize on small price movements, often using automated tools for speed.
- Strategy Example: Using order book analysis to spot supply and demand imbalances and quickly enter and exit trades, taking profits from minor fluctuations in asset prices.
What’s Your Personality Type?
- Risk Tolerance: If you’re risk-averse, consider swing or position trading. If you thrive in high-risk, high-reward environments, day trading or scalping may be more suitable.
- Time Availability: Full-time jobs are more compatible with swing or position trading, while day trading requires constant monitoring.
- Emotional Discipline: Day trading requires an ability to remain unemotional during fast-paced trades. If you find yourself overly affected by losses or gains, a slower-paced style like swing trading may suit you better.
3. Develop a Detailed Trading Plan
A trading pro always trades with a well-defined plan. This plan serves as a roadmap, helping you navigate market uncertainty, reduce emotional trading, and maintain consistency.
Components of a Winning Trading Plan
- Personal and Financial Goals:
- Short-term Goals: Focus on small, incremental achievements such as achieving a 5% return in your first month or mastering a specific strategy.
- Long-term Goals: Aim for bigger objectives such as consistently profitable trading over a year, building a diversified portfolio, or eventually transitioning to full-time trading.
- Risk Management Strategy:
- Risk Per Trade: Decide how much of your total capital you’re willing to risk on each trade (typically 1-3%). For example, if your account is $10,000, risking 1% means you would only risk $100 on a single trade.
- Maximum Drawdown: Set a limit for how much loss you’re willing to tolerate in a day or week before stopping trading. For instance, some trading pros might decide to stop trading for the day if they lose 5% of their capital.
- Entry and Exit Criteria:
- Entry Criteria: Your decision-making process should be rule-based, relying on specific triggers such as moving average crossovers, breakouts from consolidation patterns, or a fundamental catalyst like an earnings report.
- Exit Criteria: Plan when to close your trades, whether you hit a profit target or a stop-loss level. Some traders use trailing stops to protect profits while still giving the trade room to grow.
- Position Sizing:
- Use the Position Size Formula: (Account Size * Risk Percentage) / (Entry Price – Stop-Loss Price) to calculate your ideal position size based on risk.
- Adjust for volatility. If the market is particularly volatile, reduce your position size to avoid larger-than-expected losses.
- Trading Journal:
- What to Record: Each trade’s details, including entry/exit points, size, the rationale behind the trade, emotions felt during the trade, and the final result.
- Analysis: After the trade, analyze what went right or wrong. Was your stop too tight? Did you react emotionally?
4. Master Both Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Professional traders use a combination of technical and fundamental analysis to make informed trading decisions. The key is learning how to blend these two approaches in a way that aligns with your trading style.
Deep Dive into Technical Analysis
- Support and Resistance Levels:
- These are psychological price points where assets have historically found buyers or sellers. Knowing how to draw these levels on a chart allows traders to make decisions about entry or exit points based on previous price action.
- Example: If a stock continuously bounces off $50, that could be a support level. If it breaks above $60 but retreats several times, that could serve as a resistance level.
- Chart Patterns:
- Learn classic patterns such as head and shoulders, triangles, and double tops/bottoms. These patterns often signal a reversal or continuation of a trend.
- Candlestick Patterns: Candlesticks can tell stories about market sentiment. Patterns like doji and engulfing candles can give you insights into potential reversals.
- Indicators:
- Moving Averages: The simple moving average (SMA) and exponential moving average (EMA) are great for identifying trends. Many traders use a combination (e.g., 50-day and 200-day SMA) to generate signals.
- Oscillators: RSI and stochastic oscillators help identify overbought or oversold conditions.
- Bollinger Bands: Use these to gauge volatility and potential breakout points. When price touches the upper band, it may indicate an overbought condition; when it touches the lower band, it could signal oversold conditions and potential buying opportunities.
Advanced Technical Analysis Tools and Concepts
- Fibonacci Retracement:
- What It Is: Fibonacci retracement is a popular tool used by technical trading pros to predict possible support and resistance levels by measuring key price movement percentages (23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%).
- How to Use: By applying Fibonacci retracement lines to a trend, you can identify potential areas where the price might reverse or continue its direction. Traders often use it to pinpoint entry levels after a pullback in an uptrend.
- Volume Analysis:
- Why It Matters: Volume reflects the number of shares or contracts being traded in the market. High volume during a price increase could signal a strong trend, while decreasing volume might suggest a weakening move.
- Volume Indicators: Tools like the Volume Moving Average or the On-Balance Volume (OBV) indicator help traders gauge market sentiment and confirm trends.
- Advanced Candlestick Patterns:
- In addition to simple patterns like doji or engulfing, advanced traders focus on patterns such as:
- Three Black Crows: A bearish reversal pattern.
- Morning Star/Evening Star: Signals a possible reversal of an uptrend (morning star) or downtrend (evening star).
- In addition to simple patterns like doji or engulfing, advanced traders focus on patterns such as:

Deep Dive into Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis is especially useful for longer-term trading pro like position traders. It involves studying the financial health of companies, the economy, or assets you’re trading to determine their true value.
- Company-Specific Fundamentals:
- Earnings Reports: Evaluate key metrics such as earnings per share (EPS), profit margins, and revenue growth. A consistent pattern of positive earnings surprises can push a stock higher.
- Balance Sheet Health: Look for companies with low debt levels, strong cash flow, and high return on equity (ROE). These are indicators of a financially sound company.
- P/E Ratio and PEG Ratio: The price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio is widely used to determine whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued. Combine it with the price/earnings-to-growth (PEG) ratio to account for expected growth rates.
- Dividend Yield: For position traders, high and consistent dividend yields may provide additional passive income and an indication of a stable company.
- Economic Data and Macro Factors:
- Interest Rates: Pay close attention to interest rate decisions by central banks, such as the Federal Reserve. Rising rates can negatively affect stocks but may benefit currencies like the U.S. dollar.
- Inflation Data: Higher inflation usually leads to central banks increasing rates, which can affect the stock market, bond yields, and commodity prices.
- Unemployment Rates: A decreasing unemployment rate can indicate a strong economy and lead to increased consumer spending, benefiting cyclical stocks (e.g., retail, travel).
- Geopolitical Events: Stay informed about global political developments that could impact commodity prices, forex rates, and even stock indices. Events like trade wars, elections, and global pandemics can have immediate and long-lasting market effects.
Combining Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Professional traders and trading pros often blend both technical and fundamental analysis. For instance:
- Fundamental Analysis: Use to determine what to trade. For example, you may identify a fundamentally strong stock after analyzing its earnings reports and industry outlook.
- Technical Analysis: Use to decide when to trade. After identifying a strong stock, you might wait for a technical breakout from a consolidation pattern to make your move.
By using both approaches, you’ll improve your timing and asset selection, which are both crucial to becoming a successful trader.
5. Implement Effective Risk Management Strategies
No matter how proficient you become at analysis, managing risk will be the key to your long-term survival as a trader. Proper risk management separates successful traders from those who fail after a few bad trades.
Key Risk Management Techniques for Traders
- The 1% Rule:
As a rule of thumb, trading pros often risk no more than 1-2% of their capital on a single trade. This ensures that even if a trade goes against them, they still have 98-99% of their capital intact for future trades.
- Position Sizing:
Position sizing refers to determining how much of your capital to allocate to each trade. Larger position sizes may yield higher rewards but also expose you to greater risk. Use the formula:
Position Size = (Account Balance x Risk per Trade) / (Entry Price – Stop-Loss Price)
- Set Stop Losses:
A stop-loss order automatically closes a trade when the price moves against you by a predetermined amount. This protects you from catastrophic losses.

Types of Stop Losses:
- Fixed Stop Loss: You place your stop a certain percentage or dollar amount away from your entry price.
- Trailing Stop Loss: This moves with the price as the trade moves in your favor, allowing you to lock in profits while still giving the trade room to grow.
- Risk/Reward Ratios:
Aim for a minimum risk/reward ratio of 1:3. This means that for every dollar you risk, you aim to gain three dollars. By focusing on trades with favorable risk/reward ratios, you can afford a lower win rate and still be profitable.
- Diversification:
Spread your trades across different assets or markets to avoid concentrated risk. For instance, instead of investing all your capital in tech stocks, you could allocate some to commodities, bonds, or forex.
- Hedging:
Trading pros use hedging strategies to offset potential losses. For example, if you’re long on a stock, you could buy a put option to protect against a downside move. This strategy limits your losses while still giving you exposure to potential gains.
Avoid Common Risk Management Mistakes
- Overleveraging: Leverage amplifies both gains and losses. Many trading pros fail by overleveraging, meaning they borrow too much capital from their broker to trade larger positions. This increases the chances of margin calls and significant losses.
- Ignoring Correlation: Diversification doesn’t work if your assets are correlated. For example, holding multiple positions in tech stocks doesn’t offer much protection since they tend to move together. Instead, diversify across different sectors or asset classes.
- Chasing Losses: After a series of losses, traders may attempt to make up for it by increasing their position sizes or taking riskier trades. This usually leads to bigger losses and emotional decision-making. Stick to your plan and accept losses as part of the process.
6. Master Your Trading Psychology
Professional traders recognize that emotions, not strategy, often dictate success or failure. Mastering your emotions and understanding trading psychology is essential for consistent performance.
Understanding Common Psychological Pitfalls
- Fear: Fear can paralyze traders, causing them to exit trades prematurely or avoid taking trades altogether. Fear is often a result of past losses, lack of confidence in a strategy, or market volatility.
- How to Combat Fear: Trust in your trading plan and your risk management system. Set predefined exit points and stop-losses to avoid emotional decisions.
- Greed: Greed leads trading pros to overstay their trades, hoping for more profits even when the signs point to a reversal. It can also tempt traders into overleveraging or overtrading.
- How to Combat Greed: Set clear profit-taking rules and stick to them. Be content with consistent, smaller wins rather than chasing large, risky trades.
- Revenge Trading: After a losing trade, many traders feel the need to immediately recoup their losses by entering another trade without a proper setup. This emotional response leads to further losses.
- How to Avoid Revenge Trading: Accept losses as a natural part of trading. Take a break after a losing streak to regain composure.
- Overconfidence: A streak of winning trades can lead to overconfidence, causing traders to take unnecessary risks or deviate from their plan.
- How to Stay Grounded: After a winning streak, review your trades objectively. Were they based on sound strategy, or was luck involved? This reflection will help you stay humble and cautious.
Developing a Trading Mindset
- Patience: Trading pro wait for the perfect setup before entering a trade. Rather than trading constantly, they selectively enter only when the probability of success is high.
- How to Cultivate Patience: Follow a strict set of criteria for your trades. If those criteria aren’t met, sit out and wait.
- Discipline: Discipline is key to sticking to your trading plan and avoiding impulse trades. Without it, even the best strategies will fail.
- How to Build Discipline: Set rules for every part of your trading: when to enter, when to exit, and how much to risk. Use a trading journal to hold yourself accountable.
- Adaptability: Markets change, and what worked yesterday may not work tomorrow. Professional traders are constantly learning, analyzing market conditions, and adjusting their strategies accordingly.
- How to Stay Adaptable: Regularly review your trades and strategy. If market conditions shift (e.g., a transition from a bull to a bear market), be willing to change your approach.
7. Leverage Technology and Trading Tools
Modern trading pros have access to a wide array of tools and technology that can significantly enhance their performance. Using these tools effectively can give you a competitive edge in the markets.
Trading Platforms
- Brokerage Platforms: Choose a reliable and user-friendly brokerage platform that offers the features you need for your specific trading style. Top platforms offer real-time data, advanced charting tools, fast execution speeds, and low fees. Examples include MetaTrader for forex traders and thinkorswim for options and stock traders.
- Mobile Trading Apps: Mobile apps have revolutionized trading by allowing traders to execute trades on the go. Platforms such as Robinhood or TD Ameritrade’s app are equipped with essential features like notifications for price alerts, real-time market updates, and portfolio management tools.
- Automated Trading Systems: For traders looking to reduce the emotional aspect of trading, automated trading systems, also known as algorithmic trading, can be invaluable. These systems use predefined rules to execute trades automatically, removing the need for human intervention. They’re particularly popular among high-frequency traders and scalpers. Many platforms allow traders to create and test their algorithms using historical data.
- Backtesting Tools: Backtesting is the process of testing your trading strategy using historical data to see how it would have performed in the past. Platforms like TradingView and MetaTrader offer backtesting capabilities. This allows you to refine your strategy before putting real money on the line.
- Paper Trading: For new traders or those trying a new strategy, paper trading (trading with simulated money) is an excellent way to practice without risking capital. Most brokers offer a demo account with virtual funds to test strategies in real market conditions.
Market News and Research Tools
- Economic Calendars: Staying informed about upcoming economic events is crucial, especially for forex, commodity, and stock traders. Platforms like Forex Factory or Investing.com provide detailed economic calendars with information on upcoming announcements, earnings reports, and market-moving events.
- Real-Time News Platforms: Tools like Bloomberg, Reuters, or Yahoo Finance offer up-to-the-minute news on financial markets, helping trading pros stay informed about macroeconomic trends, company news, and global events that can affect asset prices.
- Social Sentiment Tools: In recent years, social sentiment analysis has become increasingly important. Platforms like StockTwits or TradeBirds track social media mentions of stocks and other assets, helping trading pros gauge market sentiment. Sentiment analysis can be especially useful for identifying trending assets early on.
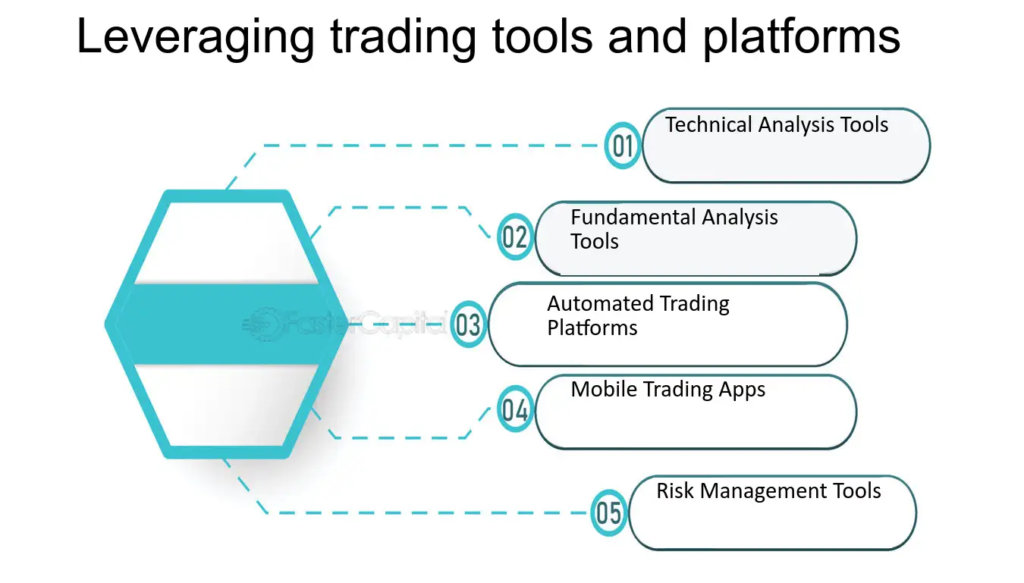
Technical Analysis Tools
- Charting Platforms: Comprehensive charting software is essential for any trader using technical analysis. Tools like TradingView, MetaTrader, or NinjaTrader offer customizable chart types, indicators, and drawing tools to perform in-depth technical analysis.
- Screeners and Scanners: Stock or forex screeners help traders identify opportunities based on predefined criteria. For instance, a screener might look for stocks with high volume breakouts or currencies showing strong momentum. Platforms like Finviz or StockFetcher allow you to filter assets by indicators, volume, price action, and more.
- Price Alerts: Set automated price alerts to notify you when an asset reaches a specific price level or triggers a technical condition, such as breaking above a key resistance level. Most trading platforms and apps offer customizable alerts via email or text message.
8. Keep a Detailed Trading Journal
A trading pro journal is an invaluable tool for growth. Every trade should be meticulously recorded and analyzed. This practice not only helps refine your strategy but also aids in keeping emotions in check and developing discipline.
What to Include in Your Trading Journal
- Trade Details:
- Entry and Exit Points: Document the exact time and price of your entry and exit for each trade.
- Position Size: Record how much capital you allocated to the trade, including leverage (if applicable).
- Risk/Reward: Note the risk/reward ratio before entering the trade. Did the trade meet your criteria?
- Market Conditions:
- Market Sentiment: Was the market trending or in a range? Were there any significant news events that influenced your decision?
- Volume: Did the trade take place in high or low-volume conditions?
- Indicators Used: Document any technical indicators or chart patterns that influenced your decision to enter or exit the trade.
- Trade Outcome:
- Profit or Loss: Was the trade profitable? By how much (percentage and monetary terms)? If you took a loss, was it within your planned stop-loss level?
- How the Trade Played Out: Did the price hit your target or stop-loss? Did the market behave as you expected?
- Emotional State:
- Pre-trade Emotions: Were you feeling confident, anxious, or indifferent when entering the trade?
- During the Trade: How did you react to market movements while the trade was active?
- Post-trade Emotions: Were you satisfied with the outcome? Did you stick to your plan or deviate?

How to Analyze Your Journal
- Identify Patterns in Wins and Losses:
- After 20 or more trades, review your journal to identify common factors in both your successful and unsuccessful trades. Were there certain setups that consistently worked well? Did you often lose money on trades triggered by emotional decisions?
- Adjust Your Strategy:
- Use your journal as a tool for continuous improvement. If certain patterns or indicators frequently led to losses, consider removing them from your strategy. Conversely, double down on what works.
- Emotional Analysis:
- Review how your emotions influenced your trading decisions. If you frequently find yourself deviating from your plan due to fear or greed, implement stricter rules to control these emotions (e.g., using trailing stops or automated orders).
9. Embrace Continuous Learning and Improvement
No matter how experienced you become, the financial markets are constantly evolving. The trading pros recognize that they need to continue learning, adapting, and refining their strategies.
Stay Updated with Market Trends
- Follow Economic and Market Developments: Stay informed about global economic trends, interest rate policies, and significant geopolitical events. Market sentiment can shift based on these factors, and you need to adapt your strategy accordingly. For example, during periods of high inflation, certain asset classes like commodities may perform better than others.
- Sector Rotation: Understanding how sectors rotate during different phases of the economic cycle can give you a competitive edge. For instance, during economic expansions, cyclical sectors like technology and consumer discretionary tend to outperform, while defensive sectors like utilities and healthcare do well during recessions.
- Learn About New Trading Instruments: Financial innovation leads to new trading opportunities. Cryptocurrencies, for instance, have emerged as a popular asset class in recent years. Stay open to learning about new instruments or markets that can diversify your portfolio and offer new trading opportunities.
Continue Learning from Books and Courses
- Books:
- “Trading in the Zone” by Mark Douglas is a must-read for mastering trading psychology.
- “Market Wizards” by Jack Schwager provides insights from interviews with some of the most successful traders in history.
- “A Complete Guide to Volume Price Analysis” by Anna Coulling offers detailed explanations of using volume to confirm trends.
- Online Courses and Webinars: Many platforms, including Coursera, Udemy, and Investopedia, offer comprehensive courses on trading strategies, technical analysis, and risk management. Advanced traders may consider specialized courses on options, futures, or algorithmic trading.
- Join a Community: Surround yourself with other trading pros to share knowledge, strategies, and market insights. Joining forums or online trading communities like Elite Trader, Trade2Win, or even social media platforms can help you stay connected to the broader trading community.
Subscribe to Financial Newsletters and Podcasts
- Newsletters: Many trading pros subscribe to newsletters written by market analysts or economists. These provide expert commentary on market conditions, trends, and specific assets to watch.
- Popular Newsletters: The Daily Shot, Morning Brew, and Seeking Alpha’s Market Wrap provide timely information on stock markets, commodities, and macroeconomic conditions.
- Podcasts: Podcasts are a great way to continue learning on the go. Some popular trading podcasts include:
- Chat With Traders: In-depth interviews with professional traders and industry experts.
- The Investors Podcast: Focused on investing but often provides valuable insights into market trends and the global economy.

10. Patience and Persistence: Keys to Long-Term Success
Trading is a journey that requires both patience and persistence. While the idea of getting rich quickly through trading is alluring, true success comes from steady and consistent growth over time. Trading pro understand that losses are part of the game, and their focus is on improving their long-term performance, not winning every trade.
Focus on Long-Term Sustainability
- Realistic Expectations: Instead of aiming for home runs on every trade, focus on achieving consistent small gains that compound over time. Aiming for modest but regular returns (e.g., 2-5% per month) can lead to significant long-term wealth.
- Embrace the Learning Process: Trading is a skill that takes time to master. Accept that you will make mistakes along the way. What sets trading pro apart is their ability to learn from these mistakes, adjust their strategies, and move forward.
- Avoid Overtrading: Patience means waiting for the right trading opportunities rather than trading for the sake of being in the market. Overtrading often leads to poor decision-making, higher fees, and increased emotional pressure.
The Journey to Becoming a Trading Pro
Becoming a trading pro is a journey that involves much more than mastering a few technical indicators or developing a basic understanding of the markets. It requires a combination of education, practice, emotional discipline, risk management, and a deep commitment to continuous learning.
Key Takeaways for Aspiring Trading Pros
- Education is Essential: Start by understanding the fundamental concepts of the markets, asset classes, and trading instruments. As you progress, deepen your knowledge by mastering technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and market psychology.
- Develop Your Trading Style: Identify which trading style suits your personality, risk tolerance, and time availability. Whether you become a day trader, swing trader, position trader, or scalper, it’s important to match your strategy to your lifestyle.
- Create and Stick to a Trading Plan: A well-thought-out trading plan is crucial for consistent success. This plan should define your objectives, risk management rules, and specific entry and exit criteria. Sticking to the plan during emotional highs and lows is essential for long-term profitability.
- Master Technical and Fundamental Analysis: Blend these two approaches to increase the accuracy of your trades. Use technical analysis to time your entries and exits and fundamental analysis to choose the right assets to trade.
- Risk Management is Key: Risk management is the foundation of long-term success. Implement strategies like stop-losses, position sizing, and diversification to protect your capital. Never risk more than 1-2% of your trading capital on a single trade.
- Embrace Emotional Discipline: Emotional control is just as important as technical skill. Recognize common psychological pitfalls like fear, greed, and overconfidence, and learn strategies to mitigate their impact on your decision-making.
- Leverage Technology and Tools: Use advanced charting software, backtesting tools, automated trading systems, and economic calendars to gain an edge. Stay updated on market developments and make informed decisions using the best tools available.
- Keep a Detailed Trading Journal: A trading journal is your best tool for self-improvement. Use it to track your trades, identify patterns in your successes and failures, and refine your strategy over time.
- Never Stop Learning: The markets are constantly evolving, and so should you. Read books, attend courses, join trading communities, and listen to podcasts to keep your knowledge fresh and relevant. Embrace the idea of lifelong learning.
- Patience and Persistence: Remember that trading is a long-term endeavor. Don’t chase quick wins or overtrade out of impatience. Focus on steady growth, learn from your mistakes, and stay committed to your plan.

The Professional Trader’s Mindset
What ultimately separates trading pro from amateurs is their mindset. Professional traders approach the markets with discipline, patience, and a willingness to learn from their mistakes. They understand that losses are inevitable, but they trust their strategy and stick to their plan.
Trading pro also manage their expectations. They know that no strategy works 100% of the time and that even the best traders go through periods of drawdown. The key is to maintain emotional control, continuously improve, and focus on long-term success.
Are You Ready to Become a Trading Pro?
Trading offers incredible opportunities, but it requires a commitment to mastering both the technical and emotional aspects of the craft. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you’ll be well on your way to developing the mindset, skills, and strategies needed to become a professional trader.
Remember, success in trading doesn’t come overnight. It’s a journey filled with challenges, losses, and lessons. But with the right approach, discipline, and perseverance, the rewards—both financial and personal—can be immense.
So, whether you’re just starting or you’re refining your skills, stay focused, keep learning, and embrace the process. In time, you’ll build the expertise and confidence needed to navigate the markets like a true trading professional.
You might also be interested in – ChatGPT vs. Google Gemini: Which Is Better?


